Overview
This guide walks you through the complete process of securing your Kubernetes Ingress using cert-manager with GlobalSign’s Atlas-ACME server and the HTTP-01 challenge type. At the completion of this article, you'll learn how to:
- Set up a Kubernetes cluster with Kops and AWS
- Install and configure cert-manager
- Set up NGINX Ingress Controller
- Configure GlobalSign ACME Issuer and Certificate
- Secure an Ingress resource with a trusted TLS certificate
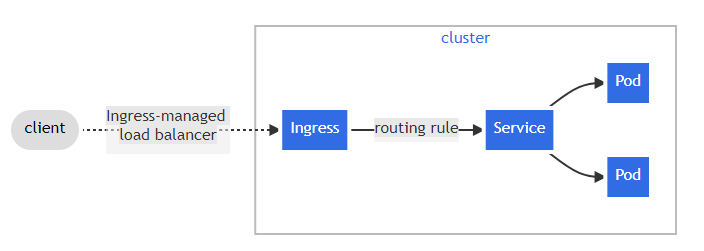
What is Ingress?
Ingress exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. Traffic routing is controlled by rules defined on the Ingress resource.
Here is a simple example where an Ingress sends all its traffic to one service:
Prerequisites
Ensure the following tools are installed and configured on your system:
- unzip
- AWS CLI
- Helm
- kubectl
- kops
- Create S3 bucket
- Create one hosted zone from Route53
Note: The name of the zone either same as bucket name or should be succeed-er of bucket name for example if bucket name is example.com then hosted zone name should be abc.example.com. - SSH key pair
Install Unzip
sudo apt install unzip
Install AWS CLI
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip" unzip awscliv2.zip sudo ./aws/install
Install Helm
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
There are few policies required to run the cluster successfully which should be assigned to a user and a role for the cluster:
IAM URL: https://console.aws.amazon.com/iamv2/home#/home
Create a user for k8s cluster and assign the below policies:
- Go to Users
- Add users
- Give a name to user
- Select Access key - Programmatic access
- Permissions
- Select Attach existing policies directly and select the below policies for this user.
a.) VPC full access
b.) EC2 full access
c.) S3 full access
d.) Route53 full access
e.) IAM full access
Create a role for k8s cluster and assign the below policies:
- Go to IAM dashboard https://console.aws.amazon.com/iamv2/home#/home
- Roles
- Create role
- Form common use case select EC2 and go to next screen for permissions
- Select the below permissions for this user
a.) VPC full access
b.) EC2 full access
c.) S3 full access
d.) Route53 full access
e.) IAM full access
Launch an Ec2-Instance and assign this role to the instance.
# kubectl
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s
https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
#make the downloaded file executable
chmod +x kubectl
#Move the executable to the /usr/local/bin
sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin
Install kops
curl -LO https://github.com/kubernetes/kops/releases/download/$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/kubernetes/kops/releases/latest | grep tag_name | cut -d '"' - f 4)/kops-linux-amd64
#Make the binary executable
chmod +x kops-linux-amd64
#Move the executable to /usr/local/bin
sudo mv kops-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/kops
In order to work further need to login with the above created programmatic user:
aws configure
#enter the Access key ID and Secret access key.
#Provide the region details i.e., us-east-1 or any other
#Give output format as "json".
#Create a S3 bucket through S3 bucket console: https://s3.console.aws.amazon.com/s3/home?region=us-east-1
#Create a private hosted zone from Route53 console: https://console.aws.amazon.com/route53/v2/home#Dashboard
#Generate public and private keys
Set Up Kubernetes Cluster
export KOPS_STATE_STORE="s3://your-s3-bucket-name"
export MASTER_SIZE=${MASTER_SIZE:-m4.large}
export NODE_SIZE=${NODE_SIZE:-m4.large}
export ZONES="us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c"
kops create cluster pki.atlasqa.co.uk --node-count 3 --zones $ZONES --node-size $NODE_SIZE --master-size $MASTER_SIZE --master-zones $ZONES --dns public --dns-zone pki.atlasqa.co.uk --cloud aws
#It will describe everything that it will create within the cluster. In next step kops will update the cluster and resources would be created.
kops update cluster --name pki.atlasqa.co.uk --yes --admin
#It will take around 20min to get all the resources ready within the cluster.
#Check the cluster status after 20min with below command
kops validate cluster --name pki.atlasqa.co.uk
The cluster is setup, there are 3 node machines running in us-east-1 region and 3 master running in us-east-1 as per the availability zones.
Install cert-manager
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
kubectl apply --validate=false -f https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.7.1/cert-manager.yaml
kubectl label namespace cert-manager certmanager.k8s.io/disable-validation=true
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo update
helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager --version v1.7.1 -n cert-manager
Install Ingress Controller
Install Nginx-ingress-controller in namespace cert-manager and create A record to your DNS Zone
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx --repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx --namespace cert-manager
Add the following to the cluster under spec of conf file to create nginx-ingress resource as the elastic load balancer.
kops edit cluster
cluster-configspec:additionalPolicies:master: |[{"Effect":"Allow","Action":"iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole","Resource":"arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-service-role/*"},{"Effect":"Allow","Action": ["ec2:DescribeAccountAttributes","ec2:DescribeInternetGateways"],"Resource":"*"}]
After adding above configuration update the cluster:
kops update cluster --name ClusterName --yes
Add an A record to your DNS zone
kubectl get svc -n cert-manager

Configure GlobalSign Atlas-ACME Issuer
Step 1: Set Up account binding key as a secret within Kubernetes
kubectl create secret generic eab-secret --from-literal secret=HMAC_key -n cert-manager
Step 2: Set up the GlobalSign as issuer/ClusterIssuer
kubectl apply -f issuer.yml -n cert-manager
issuer.ymlapiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1 kind: Issuer metadata: name: eab-issuer namespace: cert-manager spec:apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1kind: Issuermetadata:name: eab-issuernamespace: cert-managerspec:acme:email: user@example.comserver: https://******/directoryexternalAccountBinding:keyID: **************keySecretRef:name: eab-secretkey: secretkeyAlgorithm: HS256privateKeySecretRef:name: acme-account-secret-issuersolvers:- http01:ingress:class: nginx

Step 3. Create certificate resource
kubectl apply -f cert.yml -n cert-manager
cert.ymlapiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1kind: Certificatemetadata:name: eab-certnamespace: cert-managerspec:secretName: acme-account-secretduration: 2160hrenewBefore: 360hcommonName: pki.atlasqa.co.ukdnsNames:- pki.atlasqa.co.ukissuerRef:name: eab-issuer
Step 4. Securing ingress resource
ingress.yml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1kind: Ingressmetadata:annotations:cert-manager.io/issuer: eab-issuerkubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginxcert-manager.io/acme-challenge-type: http01name: nginxnamespace: cert-managerspec:rules:- host: pki.atlasqa.co.ukhttp:paths:- pathType: Prefixpath: /backend:service:name: nginxport:number:80tls:- hosts:- pki.atlasqa.co.uksecretName: hvca-cert-secret
