Overview
This guide walks you through the complete process of securing an AWS EKS Kubernetes Ingress resource with a trusted TLS certificate from GlobalSign using Cert-Manager and the GlobalSign Atlas Issuer plugin. At the completion of this article, you'll learn how to:
- Set up IAM roles and permissions
- Create and configure an EKS cluster
- Install and configure cert-manager with Atlas plugin
- Set up NGINX Ingress Controller
- Configure GlobalSign Issuer and Certificate
- Secure an Ingress resource with a TLS certificate
What is Ingress?
Ingress exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. Traffic routing is controlled by rules defined on the Ingress resource.
Here is a simple example where an Ingress sends all its traffic to one service:
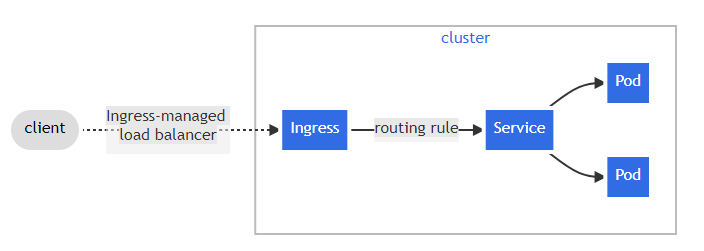
Prerequisites
Ensure the following tools are installed and configured on your system:
-
AWS Account
-
Nginx Ingress
-
One Valid Domain Name
-
Kubectl
-
Helm Package Manager
-
Cert-manager & its CRDs
-
Cert-manager-Atlas Plugin
Guidelines
-
AWS Ubuntu EC2 Instance - Use the AWS documentation for creating Ubuntu Instance
-
Create A User in IAM.
a. Go to IAM Console and select Users.
b. Click on create user.
c. Give a name to the user.
d. Fill the checkbox of "Provide user Access to the AWS Management Console".
i. Select I want to create an IAM user.
ii. In Console Password, choose Autogenerate Password or Custom Password based on your preference.
iii. Click Next in the bottom right corner.
e. In Set Permissions, choose:
i. Select Add User to a group in case if you already have defined policies for a particular user group, otherwise choose Attach Policies directly.
ii. In Permission Policies, provide the following permissions to the user. Note: You can provide permissions based on your own requirements as this is just for the example purposes.- AdministratorAccess
- AmazonEC2FullAccess
- AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
- AmazonEKSServicePolicy
- AmazonEventBridgeFullAccess
- AmazonRoute53FullAccess
- AmazonVPCFullAccess
- AWSCloudFormationFullAccess
- IAMFullAccess
iii. Click Next in the bottom-right corner.
iv. Review your User Permissions and Policies.
v. Retrieve Login URL and Password. -
Provide programmatic access to your user.
a. Go to IAM, then users.
b. Select your created user.
c. Select Security Credentials.
d. Go to Access Keys in your Security Credentials and choose Create Access Key.
e. Go to the Use Case and select AWS CLI.
f. Click Next, then Create Access Key.
g. You will get your Programmatic Access Keys from here. - Connect to your AWS ec2 instance which you have created in the Step 1.
- Once you are logged in to your instance, install the following tools:
a. Install Unzip.
sudo apt install unzip
b. Configure AWS CLI.
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install - Configure AWS CLI with the following commands and the programmatic access keys created in Step 3.
aws configure
#enter the Access key ID and Secret access key.
#Provide the region details i.e., us-east-1 or any other
#Give output format as "json".
#Generate public and private keys
ssh-keygen - Install Helm.
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh - Install kubectl and eksctl (tools to manage and interact with the kubernetes cluster).
a. Install the latest version of kubectl:
curl -LO"https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -shttps://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
#make the downloaded file executable
$chmod +x kubectl
#Move the executable to the /usr/local/bin
sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin
b. Install the latest version of eksctl:
#for ARM systems, set ARCH to: arm64, armv6 or armv7
ARCH=amd64
PLATFORM=$(uname -s)_$ARCH
curl -sLO "https://github.com/eksctl-io/eksctl/releases/latest/download/eksctl_$PLATFORM.tar.gz"
#(Optional) Verify checksum
curl -sL "https://github.com/eksctl-io/eksctl/releases/latest/download/eksctl_checksums.txt" | grep $PLATFORM | sha256sum --check
tar -xzf eksctl_$PLATFORM.tar.gz -C /tmp && rm eksctl_$PLATFORM.tar.gz
sudo mv /tmp/eksctl /usr/local/bin - Create the cluster with 3 worker node and 1 master node with the below command.
eksctl create cluster --name test-cluster --version 1.29 --region eu-west-1 --nodegroup-name linux-nodes --node-type m4.large --nodes 3
It will take around 10 to 15 mins for cluster to be ready to use. After the said time, you can check the status of the cluster by running the below command:
eksctl get cluster --region eu-west-1
When the cluster is ready with 3 node machines running in eu-west-1 region and 1 master running in eu-west-1 as per the availability zones. - Install Cert-manager and its CRDs.
a. Add and update the Jetstack Helm repository.
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io --force-update
b. Install the Cert-manager and it’s CRDs using the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.15.1/cert-manager.yaml
c. Install the GlobalSign's Certmanager-Atlas CRD. Once installed, then it is ready to handle Atlas Certificate requests.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/globalsign/atlas-cert-manager/releases/download/v0.0.1/install.yaml - Label the cert-manager namespace to disable resource validation
kubectl label namespace cert-manager certmanager.k8s.io/disable-validation=true - Install Nginx-ingress-controller in namespace cert-manager.
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx --repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx --namespace cert-manager
kubectl get svc -n cert-manager - Create A record in your Route 53 to the Hosted Zone for the below created Load Balancer IP. Note: The cluster IP is 10.100.96.178.
- As soon as the ingress-nginx-controller get the EXTERNAL-IP value with extension *.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com, add this value as A record into hosted zone. It would be in the sync within 60sec. Note: Before creating the hosted zone kindly make sure you have the valid domain.
- Creating A record over AWS Route53
a. Go to https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/route53/v2/home?region=eu-west-1#Dashboard and click on Hosted zones.
b. Click on Create hosted zone.
c. Enter the name followed by your actual domain name and make sure the Public hosted zone should be selected.
d. After creating the hosted zone, get NS record along with SOA record. Then, add the NS records into your domain registrar.
e. After adding the NS into domain registrar, your hosted zone is now ready to accept traffic. You can now create the A record into the hosted zone:
i. Into your hosted zone, click on Create record.
ii. In the next screen, make sure that Record Type is "A" and Alias are selected. Also, make sure that Route traffic to, Alias to Application and Classic Load Balancer are selected. After selecting the required fields, click Create records.
iii. The record would be created and it would take around 60sec to get in the sync. - Create GlobalSign Issuer to issue a TLS certificate for your Ingress with the following steps.
a. Create a secret to store the GlobalSign's ATLAS account api_key, secrets along with mTLS and private key. Note: You can get these API credentials from GlobalSign Team.
kubectl create secret generic issuer-credentials --from-literal=apikey=$API_KEY --from-literal=apisecret=$API_SECRET --from-literal=cert="$(cat mTLS.pem)" --from-literal=certkey="$(cat privatekey.pem)" -n cert-manager
b. Create an Issuer of GlobalSign.
cat <apiVersion: hvca.globalsign.com/v1alpha1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: gs-issuer
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
authSecretName: "issuer-credentials"
url: "https://emea.api.hvca.globalsign.com:8443/v2"
EOF
c. Create Certificate Resource with the following configuration:
cat <apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: pki.atlasqa.co.uk
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
# Secret names are always required.
secretName: www.atlasqa.co.uk
duration: 2160h # 90d
renewBefore: 360h # 15d
subject:
# organizations:
# - jetstack
# The use of the common name field has been deprecated since 2000 and is
# discouraged from being used.
commonName: pki.atlasqa.co.uk
isCA: false
privateKey:
algorithm: RSA
encoding: PKCS1
size: 2048
usages:
- server auth
#- client auth
# At least one of a DNS Name, URI, or IP address is required.
# dnsNames:
# -
#www.atlasqa.co.uk
# Issuer references are always required.
issuerRef:
name: gs-issuer
# We can reference ClusterIssuers by changing the kind here.
# The default value is Issuer (i.e. a locally namespaced Issuer)
kind: Issuer
# This is optional since cert-manager will default to this value however
# if you are using an external issuer, change this to that issuer group.
group: hvca.globalsign.com
EOF
d. At times the certificate object can take couple of seconds to become ready.
- Secure nginx ingress resource using the below configuration:
cat <apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: cert-manager
annotations:
cert-manager.io/issuer: GS-issuer
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- pki.atlasqa.co.uk
secretName: www.atlasqa.co.uk
rules:
- host: pki.atlasqa.co.uk
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: example-service
port:
number: 80
EOF
